Air Curtain Technology
04.
Air curtains: Technology
On open doorways with two adjacent areas with different environmental conditions, the air is interchanged between the areas because there is a tendency to equalize the temperature and pressure difference between both sides.
Air transfer on doorways happens due to these 3 factors:
-
TEMPERATURE DIFFERENCE: Natural convection effect creates an air transfer between two areas with temperature differences. Warm air will transfer through the top of the doorway and will be replaced by cold air coming in at the bottom of the doorway. Larger temperature differences create more significant air infiltration and energy losses.
-
PRESSURE DIFFERENCE: It is recommended to equalize the pressure differences between two areas as much as possible since this can affect air curtain performance. But in some installations like clean rooms, a little pressure difference helps to prevent the ingress of dust and particles from one area to another.
-
WIND, STACK EFFECT, AND DRAFTS: By modifying the air jet strength and the outlet discharge angle, the air curtain can work against forced-air movements like wind or drafts. But if the velocity of the incoming air is excessive, the air curtain will become less efficient.
Schematic representation of the main parameters involved in the performance of an air curtain produced by the UPC (Polytechnic University of Catalonia).
The efficiency of an air curtain depends on the optimization of performance factors.
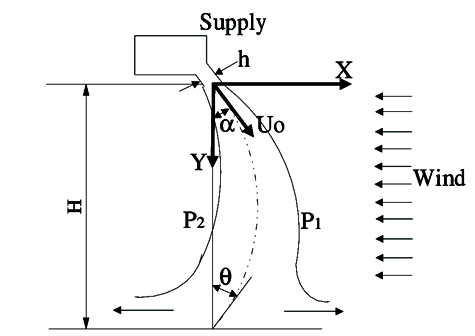
h = Effective width of the jet; α = discharge angle; U0 = Discharge velocity; θ = Negative impact angle; H = Opening height; P1 = Outside pressure; P2 = Inside pressure
The most important factors are:
JET TURBULENCE: a low turbulence jet of air will be much more efficient and save more energy.
AIRSPEED: air velocity should be adequate enough across the doorway.
AIR VOLUME: a wider jet of air makes the air curtain stronger against air transfer through doorways.
Angle discharge: if jets of air are angled correctly, it will increase the energy savings.
FAN TYPE: axial, tangential wheel, centrifugal, etc. Higher pressure fans create a higher pressure jet that reaches farther. For instance, if we compare an air curtain with a tangential fan against an air curtain with a centrifugal fan (with the same air volume), the jet of air from centrifugal fans will be stronger and larger.
UPC University air curtain studies have proven that air turbulences are one of the most important parameters that will affect the distance of the air jet.
UPC University schema shows the air turbulences behavior:
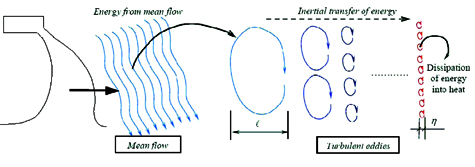
The optimized shape of the outlet plenum, the position, fan type, outlet grille shape, etc., substantially affects the air jet performance.
Air curtains angle discharge
Tests and University studies have proven that the angled discharge from an air curtain can help substantially with overall efficiency.
When factors like wind, temperature, or pressure difference cause air transfer from outside to inside, the air jet can be angled towards the outside to some degree. This helps further with preventing the penetration of air from outside.
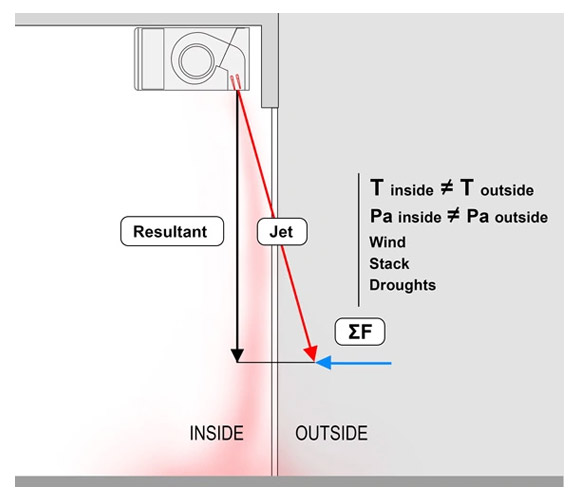
The following diagrams show the difference between air curtains with fixed outlet grilles vs. adjustable ones.
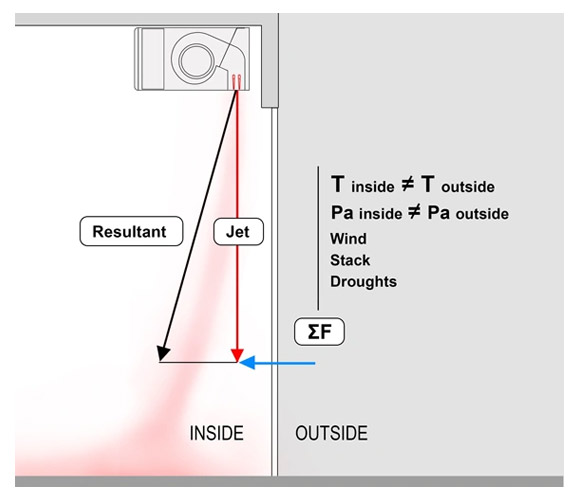
( Pic. 1 ) Fixed vanes, where the entrance air velocity pushes the jet of the air toward the inside environment. This allows some outside air to enter inside.
( Pic. 2 ) Adjustable vanes, when angled or aimed more to the outdoors, helps prevent outdoor air penetration. This means that outside air does not enter, inside air does not escape, and inside temperatures are more easily maintained.
Explore our full range of energy-efficient air curtains designed to enhance your HVAC system and improve IAQ. View our air curtain products here.
